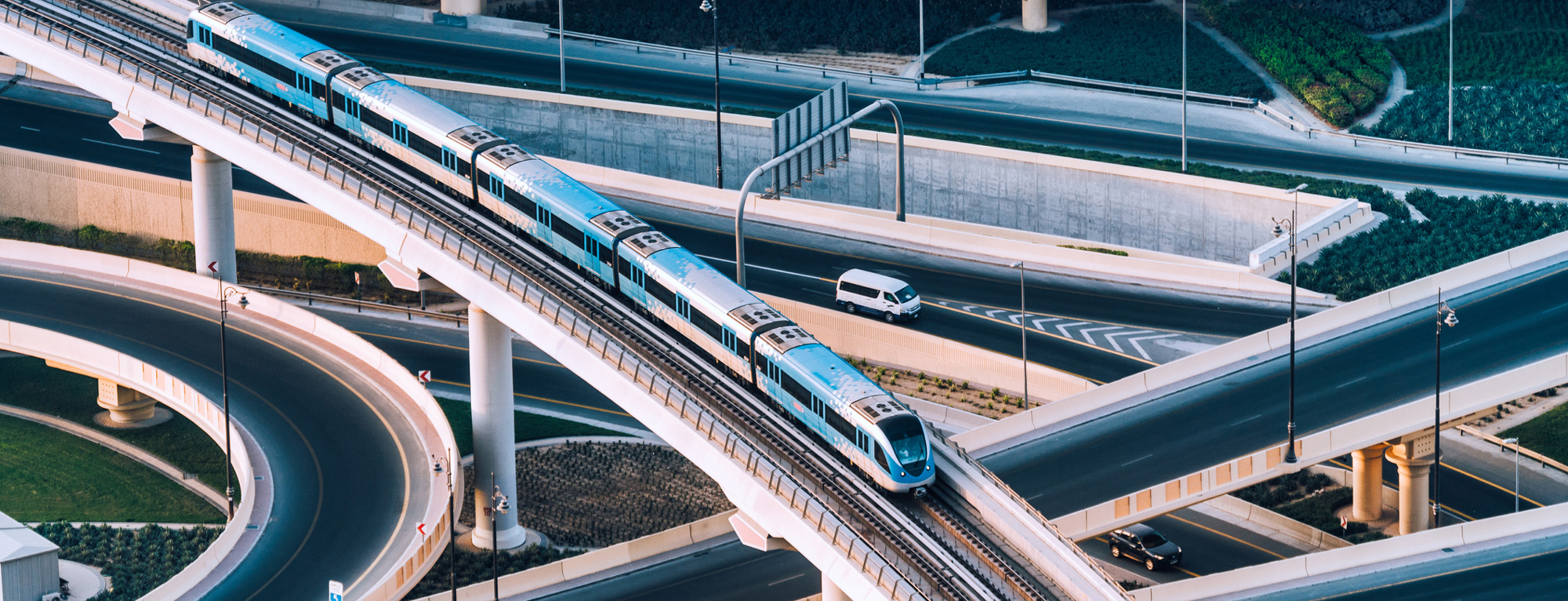
Countries lose over one-third of potential benefits from infrastructure investment due to inefficiencies. Strong infrastructure governance can reduce more than half of these inefficiencies. The IMF can help countries strengthen infrastructure governance.
Learn more about the IMF's Role in Infrastructure Governance →
PUBLICATIONS
Strengthening Infrastructure Governance for Climate-Responsive Public Investment (Climate PIMA)
Explore Our Infrastructure Governance Work
Explore by Region
Note: Country borders or names do not necessarily reflect the IMF’s official position.
⚠ Some users may experience reduced functionality using Internet Explorer. For the optimal experience, use Chrome or another alternative browser.
The Public Investment Management Assessment (PIMA) Framework
The PIMA framework examines 15 institutions of public investment in each participating country.
(Click on the interactive chart to explore)
Loading...
1.
Fiscal Targets and Rules:
1.a. Is there a target or limit for government to ensure debt sustainability?
1.b. Is fiscal policy guided by one or more permanent fiscal rules?
1.c. Is there a medium-term fiscal framework (MTFF) to align budget preparation with fiscal policy?
2.
National and Sectoral Planning:
2.a. Does the government prepare national and sectoral strategies for public investment?
2.b. Are the government’s national and sectoral strategies or plans for public investment costed?
2.c. Do sector strategies include measurable targets for the outputs and outcomes of investment projects?
3.
Coordinating Between Entities:
3.a. Is capital spending by SNGs, coordinated with the central government?
3.b. Does the central government have a transparent, rule-based system for making capital transfers to SNGs, and for providing timely information on such transfers?
3.c. Are contingent liabilities arising from capital projects of SNGs, PCs, and PPPs reported to the central government?
4.
Project Appraisal:
4.a. Are major capital projects subject to rigorous technical, economic, and financial analysis?
4.b. Is there a standard methodology and central support for the appraisal of projects?
4.c. Are risks taken into account in conducting project appraisals?
5.
Alternative Infrastructure Financing:
5.a. Does the regulatory framework support competition in contestable markets for economic infrastructure (e.g., power, water, telecoms, and transport)?
5.b. Has the government published a strategy/policy for PPPs, and a legal/regulatory framework which guides the preparation, selection, and management of PPP projects?
5.c. Does the government oversee the investment plans of public corporations (PCs) and monitor their financial performance?
6.
Multiyear Budgeting:
6.a. Is capital spending by ministry or sector forecasted over a multiyear horizon?
6.b. Are there multiyear ceilings on capital expenditure by ministry, sector, or program?
6.c. Are projections of the total construction cost of major capital projects published?
7.
Budget Comprehensiveness and Unity:
7.a. Is capital spending mostly undertaken through the budget?
7.b. Are all capital projects, regardless of financing source, shown in the budget documentation?
7.c. Are capital and recurrent budgets prepared and presented together in the budget?
8.
Budgeting for Investment:
8.a. Are total project outlays appropriated by the legislature at the time of a project’s commencement?
8.b. Are in-year transfers of appropriations (virement) from capital to current spending prevented?
8.c. Is the completion of ongoing projects given priority over starting new projects?
9.
Maintenance and Funding:
9.a. Is there a standard methodology for estimating routine maintenance needs and budget funding?
9.b. Is there a standard methodology for determining major improvements (e.g. renovations, reconstructions, enlargements) to existing assets, and are they included in national and sectoral investment plans?
9.c. Can expenditures relating to routine maintenance and major improvements be identified in the budget?
10.
Project Selection:
10.a. Does the government undertake a central review of major project appraisals before decisions are taken to include projects in the budget?
10.b. Does the government publish and adhere to standard criteria, and stipulate a required process for project selection?
10.c. Does the government maintain a pipeline of appraised investment projects for inclusion in the annual budget?
11.
Procurement:
11.a. Is the procurement process for major capital projects open and transparent?
11.b. Is there a system in place to ensure that procurement is monitored adequately?
11.c. Are procurement complaints review process conducted in a fair and timely manner?
12.
Availability of Funding:
12.a. Are ministries/agencies able to plan and commit expenditure on capital projects in advance on the basis of reliable cash-flow forecasts?
12.b. Is cash for project outlays released in a timely manner?
12.c. Is external (donor) funding of capital projects fully integrated into the main government bank account structure?
13.
Portfolio Management and Oversight:
13.a. Are major capital projects subject to monitoring during project implementation?
13.b. Can funds be re-allocated between investment projects during implementation?
13.c. Does the government adjust project implementation policies and procedures by systematically conducting ex post reviews of projects that have completed their construction phase?
14.
Management Project Implementation:
14.a. Do ministries/agencies have effective project management arrangements in place?
14.b. Has the government issued rules, procedures and guidelines for project adjustments that are applied systematically across all major projects?
14.c. Are ex post audits of capital projects routinely undertaken?
15.
Monitoring of Public Assets:
15.a. Are asset registers updated by surveys of the stocks, values, and conditions of public assets regularly?
15.b. Are nonfinancial asset values recorded in the government financial accounts?
15.c. Is the depreciation of fixed assets captured in the government’s operating statements?
 |
Cross-Cutting Institutions Legal Framework, IT System, Staff Capacity |
 |
PIMA is a comprehensive framework to assess infrastructure governance practices for countries at all levels of economic development. PIMA evaluates 15 institutions involved in the three key stages of the public investment cycle: planning, allocation and implementation. PIMA also assesses three cross-cutting factors that often impact the overall effectiveness of public investment management: IT system, legal frameworkand, and staff capacity.
Furthermore, as countries are increasingly interested in mobilizing private sector resources for public investment, the IMF is helping countries assess the potential fiscal costs and risks arising from Public Private Partnerships (PPPs).